Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. This condition affects approximately 1% of the world’s population and can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. Exploring the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for RA is essential for effectively managing this condition and improving patient outcomes.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
RA often presents with a variety of symptoms that can vary in severity and may fluctuate over time. Common symptoms include:
Joint Pain and Stiffness: Joint pain and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity, are hallmark features of RA. This stiffness often lasts for more than an hour.
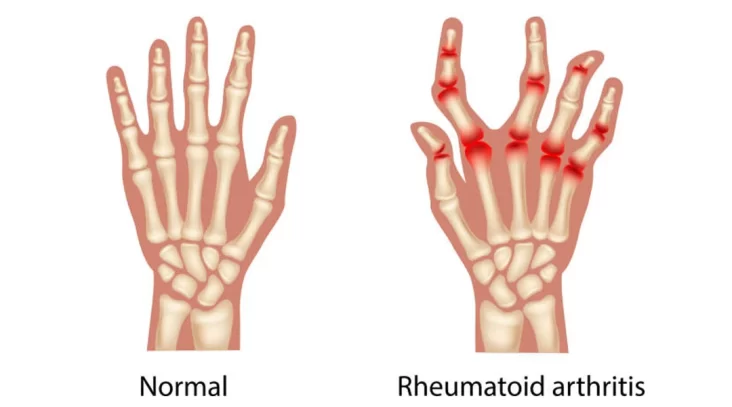
Swelling and Tenderness: Affected joints may appear swollen, warm to the touch, and tender, making movement difficult and painful.
Symmetrical Joint Involvement: RA typically affects joints on both sides of the body symmetrically, such as the wrists, knees, and ankles.
Fatigue: Many individuals with RA experience persistent fatigue, which can be debilitating and impact daily activities.
Systemic Symptoms: In addition to joint-related symptoms, RA can also affect other organs and systems in the body, leading to symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and dry eyes or mouth.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The exact cause of RA remains unclear, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors is believed to contribute to its development:
Genetics: Certain genetic variations increase the risk of developing RA. Individuals with a family history of the disease are more likely to develop RA themselves.
Autoimmune Response: RA is considered an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In RA, the immune system targets the synovium—the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints—resulting in inflammation and joint damage.
Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors, such as smoking, exposure to certain infections, and hormonal changes, may trigger the onset of RA in genetically susceptible individuals.
Abnormal Immune Response: Dysregulation of the immune system leads to the production of autoantibodies, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), which contribute to the inflammatory process in RA.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
While there is currently no cure for RA, treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve joint function. Treatment plans are often individualized based on the severity of symptoms and disease activity. Common treatment modalities include:
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine, target the underlying immune response to slow disease progression.
- Biologic agents, including TNF inhibitors and IL-6 inhibitors, target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and joint damage.
- Corticosteroids may be used to quickly alleviate symptoms during flare-ups, but long-term use is limited due to potential side effects.
Physical Therapy:
- Exercise programs designed by physical therapists help improve joint flexibility, strength, and overall function.
- Assistive devices, such as splints and braces, can provide support and reduce stress on affected joints.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Quitting smoking is crucial, as smoking has been linked to increased disease severity and reduced response to treatment in RA patients.
Surgery:
- In cases of severe joint damage and disability, surgical interventions such as joint replacement surgery (arthroplasty) may be necessary to restore function and alleviate pain.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and systemic symptoms. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic, environmental, and immune factors contribute to its development. Treatment strategies at Sujata Birla Hospital in Nashik focus on symptom management, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life through a combination of medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and surgical interventions when necessary. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for optimizing outcomes and minimizing long-term joint damage in individuals living with RA.