Make an Appointment
Celiac disease is an immune reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and other grains. It is also known as
celiac sprue
or gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
Gluten causes an immunological response in your small intestine if you have celiac disease. Over time, this process damages the lining of your small intestine, preventing some nutrients from being absorbed (malabsorption). Diarrhoea, lethargy, weight loss, bloating, and anaemia are common symptoms of intestinal injury, which can progress to significant consequences.
In addition to causing the symptoms seen in adults, malabsorption in children can impact growth and development. Celiac disease has no cure, although most people can manage their symptoms and encourage intestinal healing by eating a gluten-free diet.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Symptoms and indications of celiac disease differ greatly between children and adults. The following digestive signs and symptoms may be experienced by adults:
- Diarrhoea
- Fatigue
- Loss of weight
- Gas and bloating
- Abdominal ache
- Vomiting and nausea
- Constipation
Children with celiac disease are more likely than adults to develop digestive problems, such as:
- Vomiting and nausea
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Constipation
- Gas
- Pale, foul-smelling faeces
Causes of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including your genes, gluten-containing foods, and others, but the specific cause is unknown. Infant feeding practices, gastrointestinal diseases, and gut flora all have the potential to play a role. After surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, viral infection, or extreme mental stress, a celiac disease might become active.
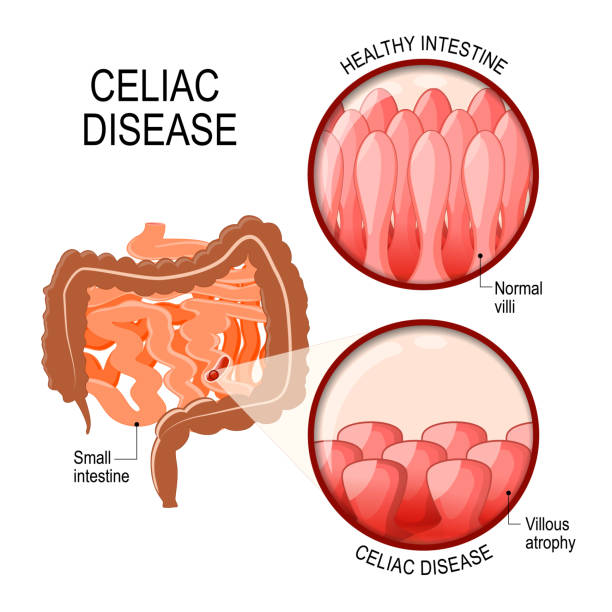
The tiny, hair like projections (villi) that line the small intestine are damaged when the body’s immune system overreacts to gluten in the diet. Vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients are absorbed by villi from the food you ingest. If your villi are damaged, no matter how much you eat, you would not get adequate nutrition.
Complications
If left untreated, celiac disease can cause a lot of complications:
- Malnutrition – Celiac disease, if left untreated, can lead to malnutrition. If your small intestine can’t absorb enough nutrition, this happens. Anaemia and weight loss can be caused by malnutrition. Malnutrition can cause stunted growth and small stature in children.
- Bone deterioration – Calcium and Vitamin D malabsorption can cause bone softening in youngsters (osteomalacia or rickets) and loss of bone density in adults (osteopenia or osteoporosis).
- Infertility and miscarriage – These are two common causes of infertility. Calcium and vitamin D malabsorption might cause reproductive problems.
- Lactose intolerance – It is a condition in which a person is unable to digest lactose. After eating or drinking lactose-containing dairy products, you may experience abdominal pain and diarrhoea due to damage to your small intestine. You might be able to accept dairy products again once your intestine has recovered.
- Cancer – Celiac disease patients who do not follow a gluten-free diet are at a higher risk of acquiring cancers such as intestinal lymphoma and small intestine cancer.
- Nervous system issues – Celiac disease can cause difficulties such as seizures or nerve damage in the hands and feet in certain people (peripheral neuropathy).

4 Comments
Pingback: Celiac Disease – Sujata Birla Hospital
Pingback: 5 Common Myths About Healthy Nutrition | Birla Healthcare
Kavin
Hi, I am Kavin, it’s my first time to commenting anywhere when I read In this paragraph, I thought I could also make comment due to this sensible post.
Pingback: A Guide To Keep Your Bones Healthy | Sujata Birla Hospital