Fungal infections, caused by an overgrowth of fungi in the body, can affect various areas such as the skin, nails, genitals, and internal organs. Common types include ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections. Symptoms range from itching and redness to more severe complications, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Antifungal medications, either topical or oral, are often prescribed for treatment. Maintaining good hygiene practices, keeping affected areas dry, and avoiding predisposing factors are crucial in prevention. Seeking prompt medical attention for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is essential to manage fungal infections effectively and prevent their recurrence.
There are several types of fungal infections, affecting different parts of the body. Common types include
- Skin Infections:
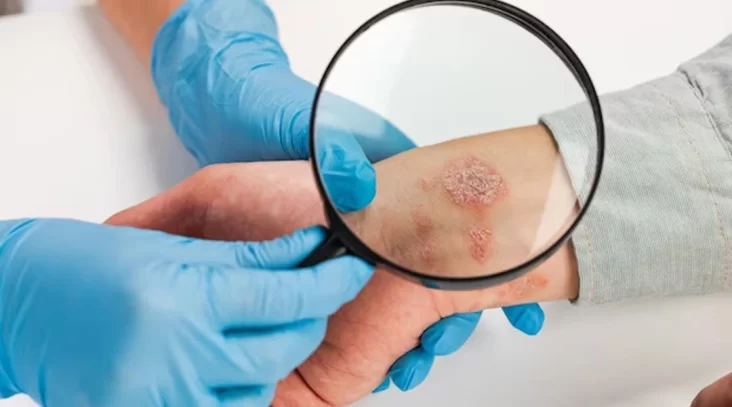
- Ringworm (Tinea corporis): This is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the body, causing a red, circular rash.
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea pedis): Affecting the feet, it often causes itching, burning, and cracking of the skin, especially between the toes.
- Nail Infections:
- Onychomycosis: Fungal infection of the nails, usually toenails, leading to discolouration, thickening, and brittleness.
- Oral and Esophageal Infections:
- Oral Thrush: Caused by Candida, it results in white, creamy lesions on the tongue and inner cheeks.
- Esophageal Candidiasis: Candida infection of the oesophagus, common in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Systemic Infections:
- Systemic Candidiasis: Candida infection that spreads throughout the body, often affecting the bloodstream and internal organs.
- Lung Infections:
- Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP): Caused by a fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii, it primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- Genital and Vaginal Infections:
- Yeast Infections: Common in women, these infections are caused by the overgrowth of Candida in the vaginal area, leading to itching, burning, and discharge.
Treatment for fungal infections varies depending on the type and severity of the infection. Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, are commonly used. Maintaining good hygiene practices, keeping the affected area clean and dry, and avoiding factors that promote fungal growth (such as warm and moist environments) can help prevent these infections.
If you suspect you have a fungal infection, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can provide guidance based on the specific type and location of the infection.

One Comment
Pingback: Fungal Infections – Sujata Birla Hospital