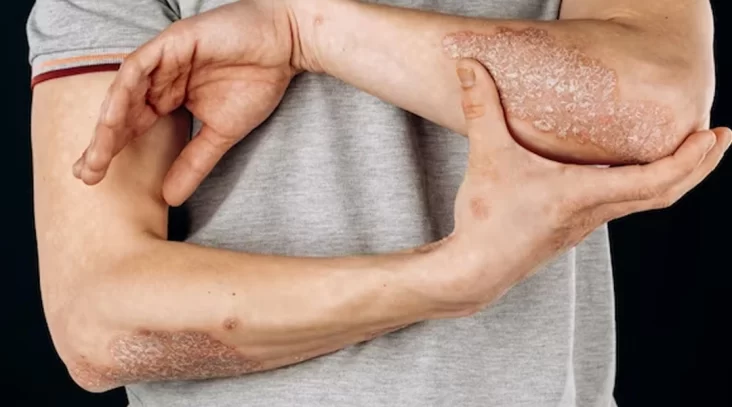
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. It is a non-contagious condition that can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers.
Psoriasis symptoms range in intensity and might include
- Red patches of skin with thick, silvery scales.
- Skin that is dry and cracked and may bleed or itch.
- Soreness or burning sensation in affected areas.
- Pitted or ridged nails.
- Joint pain or stiffness (in some cases of psoriatic arthritis).
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, several treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Treatment approaches for psoriasis include:
Topical treatments: These include creams, ointments, lotions, and foams applied directly to the affected skin. They can help reduce inflammation, itchiness, and scaling. Common topical medications include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, retinoids, and calcineurin inhibitors.
Phototherapy: This treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light, either natural sunlight or artificial light sources. Skin cell growth can be slowed down and inflammation can be decreased by phototherapy. Narrowband UVB and PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) are common forms of phototherapy used for psoriasis.
Systemic medications: For moderate to severe psoriasis that doesn’t respond to topical treatments, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system or target specific inflammatory pathways involved in psoriasis. Examples include methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin, and biological drugs like TNF inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors, and PDE4 inhibitors.
Lifestyle modifications: Changes to one’s way of life can help manage psoriasis symptoms. These include avoiding triggers such as stress, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and certain medications. Keeping the skin well-moisturized, taking regular baths, and using gentle soaps can also be beneficial.
It’s important to work closely with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan for psoriasis. They can assess the severity of your condition, consider your overall health, and tailor the treatment approach accordingly. Additionally, ongoing management and regular follow-ups are essential to ensure optimal control of symptoms and minimize flare-ups.

One Comment
Pingback: Psoriasis – Sujata Birla Hospital